Hyperthyroidism Information and Treatment
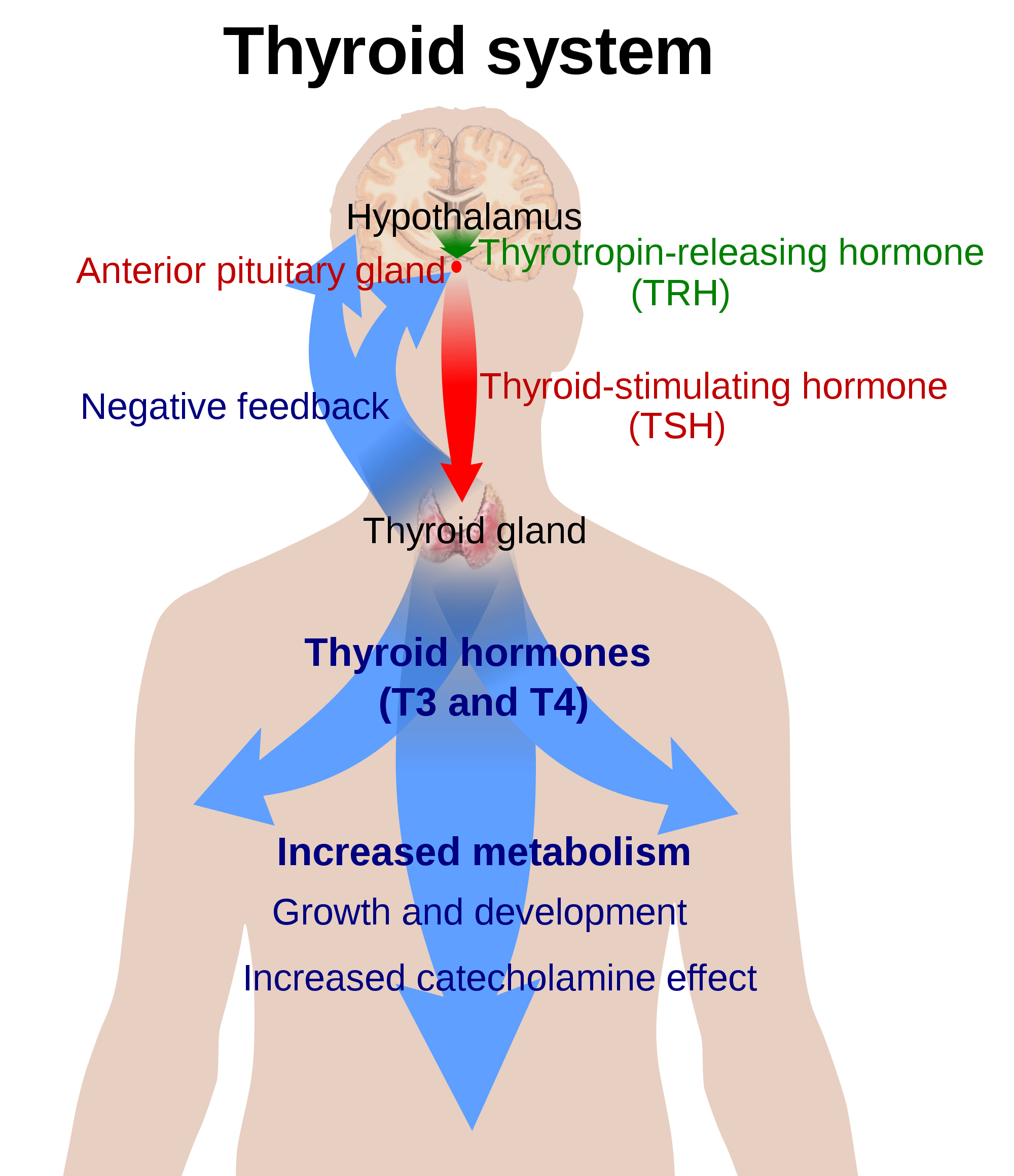 Hyperthyroidism affects approximately 1.2 percent of the US population, and can lead to debilitating symptoms for many. Numerous conditions including Graves’ disease, toxic adenoma, thyroid nodules, toxic multinodular goiter and thyroiditis can cause Hyperthyroidism. The early stages of Hashimotos thyroiditis and postpartum thyroiditis often present as Hyperthyroid as well. Graves’ disease is an autoimmune condition and is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, with 70-80% of cases due to Graves’.
Hyperthyroidism affects approximately 1.2 percent of the US population, and can lead to debilitating symptoms for many. Numerous conditions including Graves’ disease, toxic adenoma, thyroid nodules, toxic multinodular goiter and thyroiditis can cause Hyperthyroidism. The early stages of Hashimotos thyroiditis and postpartum thyroiditis often present as Hyperthyroid as well. Graves’ disease is an autoimmune condition and is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, with 70-80% of cases due to Graves’.
Symptoms of hyperthyroid/Graves disease
- Excess sweating
- Increased hunger
- Fatigue
- Heat intolerance
- Hyperactivity
- Irritability
- Restlessness
- Nervousness/anxiety/panic attacks
- Palpitations or increased heart rate
- Insomnia
- Irregular or light periods
- Puffy or protruding eyes
- Weight loss
- Hair loss
- Diarrhea
- Infertility
- Tremor
- Goiter
- Depression
Natural Treatment for Hyperthyroid
While severe hyperthyroidism is well controlled by conventional medicine, many patients with milder presentations don’t meet the criteria for treatment and are left with significant symptoms. Many patients who do opt for Western Medical treatment find that they feel less than well while on medication, and even when symptoms are controlled the underlying factors leading to hyperthyroidism are not addressed. Natural treatment options can both help with symptomatic relief in milder cases and test for and resolve many of the root causes of hyperthyroidism such as the following.
- Gut issues such as dysbiosis, leaky gut, SIBO, parasite or yeast overgrowth
- Nutrient deficiencies- Many are possible, but commonly Vit D, selenium, B vitamins, zinc, magnesium, iron or ferritin
- HPA axis (Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal) disorders- adrenal stress can increase inflammatory cytokines, reduce conversion of T4 to T3, weaken immune barriers in the lungs/GI tract/Brain and decrease sensitivity of thyroid receptor sites
- Toxicity-Plastics, chemicals and heavy metals are all common endocrine disruptors
- Food sensitivities-hyperthyroid is linked to gluten sensitivity as well as issues with many other foods
- Blood sugar issues
- Therapeutic/ healing diet
- Acupuncture can be used to reduce inflammation and enhance T regulatory cell function to balance the immune system
- Sex hormone issues
- Screening for autoimmune reactions to other body tissues
- Botanical medicine-herbs that temporarily block the activity of thyroid hormones can be used while the root causes of the condition are investigated
Testing for Hyperthyroidism
A diagnosis of hyperthyroidism is often suspected based on symptom presentation and family history, but requires lab testing confirm.
- TSH-nearly always tests low in hyperthyroidism
- T3 and T4 (thyroid hormones)- high when the thyroid is overactive
- Antibody testing including TSI, anti TSH receptor, TPO and TG help confirm an autoimmune cause and differentiate between Graves’ and Hashimotos Thyroiditis
- Thyroid Ultrasound and Iodine thyroid scan- screen for nodules that may be causing excess thyroid hormone levels
What is autoimmunity?
According to researcher and gastroenterologist Dr Alessio Fasano, three distinct factors must be present for a person to develop autoimmunity. They are genetic susceptibility, intestinal permeability, and autoimmune triggers. Intestinal permeability refers to a weakening in the cells that line the intestines. Once they are damaged, particles like food and bacteria can get into circulation and create confusion in the immune system. This leads to the body attacking its own tissues as though they were foreign invaders. Once triggers are removed and intestinal permeability has been healed we can expect both symptomatic improvement and slowing or reversal of the autoimmune disease process. Because having Graves’ disease comes with an elevated risk for developing autoimmunity to other tissues in the body, it’s important to address the underlying triggers that allow the autoimmune process to develop.
Triggers for Graves’ disease:
- Pregnancy/Perimenopause/Puberty
- Diet
- Infections
- Intestinal permeability
- Environmental toxins
- Stress
- Iodine
- Gluten
- Imbalanced estrogen levels
- Heavy metals
Please call today for more information or to schedule an appointment at (831) 239-2623. We look forward to the opportunity to help!




